What Is Avalanche (AVAX)?
Avalanche is an open-source platform for building decentralised applications (dApps) in one interoperable, decentralised, and highly scalable ecosystem.
Launched in 2020, the blockchain has emerged as a layer 1 protocol that allows crypto enthusiasts to “build anything they want, any way they want” with low-code tooling and configurability that Avalanche offers.
Avalanche raised $42M through the July 2020 Initial Coin Offering (ICO), and one year later, the Avalanche Foundation made another token sale raising $230M from large venture capital companies like Polychain and Three Arrows Capital.
Avalanche Overview
These statistics are on all indexed Avalanche L1s (as of January 2025):
- Number of transactions: 96,482,638
- Max TPS Observed: 541
- Number of active addresses:2,683,845
- Monthly Gas Usage: 48,167,889,338,052
- Unique Contract Deployers: ~15,461,429
How Does Avalanche (AVAX) Work?
As Avalanche is a network of blockchain, so the platform is quite complex. However, to break it down, there are three primary aspects of Avalanche’s architecture – it’s mechanism, its subnetworks, and multiple built-in blockchains.
Avalanche Consensus
Avalanche Consensus is a consensus mechanism that combines both classical (traditional consensus protocols that rely on all-to-all communication to ensure that all correct nodes reach the same decisions with absolute certainty) and Nakamoto consensus mechanisms (with the rise of Bitcoin) to create a novel Snow consensus protocol.
Inspired by gossip algorithms, this protocol gains its properties through a deliberately metastable mechanism. When a user initiates a transaction, it is first received by a validator node, which then randomly selects a small group of other validators to check for consensus. This process is repeated multiple times, with validators continually communicating—or “gossiping”—until a network-wide agreement is reached.
Through this iterative sampling, one validator’s message propagates to others, which in turn engages more validators, expanding the process until consensus is established across the entire system. Much like how a single snowflake can trigger an avalanche, a single transaction can ultimately gain acceptance across the network.
Validator rewards are determined based on two factors: Proof of Uptime, which tracks how long a node has staked its tokens, and Proof of Correctness, which assesses whether the node has consistently adhered to the protocol’s rules.
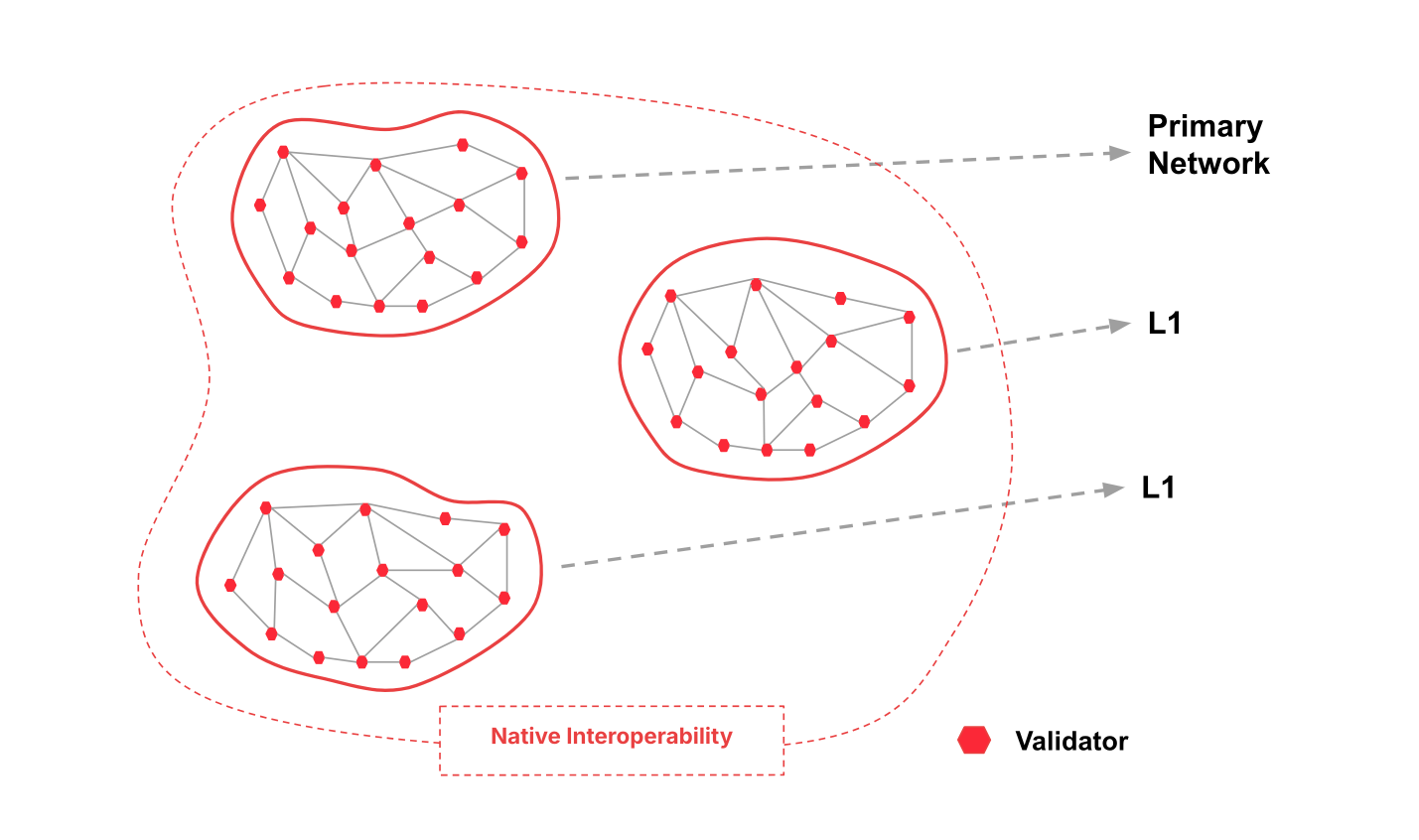
Avalanche Subnetworks
Avalanche users can create specialised chains that operate with their own principles. This characteristic offers similar benefits to other major blockchain scaling solutions such as Polkadot’s parachains and Ethereum 2.0’s shards.
Consensus on these networks can be reached by subnets, which are groups of nodes that participate in validating a designated set of blockchains. Remember that all subnet validators must also validate Avalanche’s Primary Network.
Avalanche Built-in Blockchains
The main innovation behind the Avalanche platform is the merging of three distinct blockchains to offer a diverse range of networks and utilities. Such a distinctive design approach provides the AVAX network with the necessary advantages in terms of finality.
Each blockchain (subnetwork) in the AVAX ecosystem is responsible for a different function, and this can simultaneously achieve the appropriate scalability, decentralisation, and security levels.
Exchange Chain (X-Chain)
Also known as X-Chain, Exchange Chain is the distributed ledger technology used to develop assets on the AVAX blockchain and to facilitate asset transactions. AVAX coin, the network’s native token, is now the most popular cryptocurrency on the blockchain platform.
In contrast, other decentralised exchange tokens such as JOE, compete for widespread adoption. All X-chain transactions demand users to pay transaction fees in AVAX tokens. This is similar to the way of paying Ethereum gas costs when using ETH.
Contract Chain (C-Chain)
The Contract Chain or C-chain is the next key aspect of the Avalanche cryptocurrency platform’s operation. Smart contracts are a crucial feature of the AVAX blockchain technology since they facilitate the creation of decentralised applications. At the same time, developers also make use of the platform’s scalability and security features. The contract chain executes smart contracts on the Avalanche blockchain and is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine.
The EVM compatibility in C-chain enables the deployment of Ethereum smart contracts on the AVAX blockchain. Developers can access Avalanche capabilities using conventional Ethereum development tools. What relevance does this have in the crypto space? Numerous well-known Ethereum-based applications, particularly in the DeFi industry, such as Aave, benefit from deploying a variation of their product on the AVAX network.
Platform Chain (P-Chain)
The platform chain or P-chain is the third component of Avalanche or AVAX’s primary invention. The P-chain’s fundamental goal is to enable anybody to develop layer 1 and layer 2 blockchain solutions. Users also build groups of L1 or L2 blockchain solutions.
In the Avalanche universe, such blockchains are referred to as subnets, with the P-chain serving as the default subnet. The P-chain aids in the landscape management of several Avalanche subnets by monitoring validators. Interestingly, subnets also assume responsibility for the P-validation. chain’s
AVAX – The Native Token of Avalanche
The native token of the Avalanche blockchain is $AVAX, which will be used for all important activities of the Avalanche Retro 9000 ecosystem (the primary ecosystem of Avalanche).
Tokenomics
$AVAX has a capped supply of 720,000,000 (720M) tokens. The Genesis block will have 360M $AVAX tokens, and the rest will be constantly minted as a reward to validators. Validators earn these rewards at the end of their staking period as an incentive for maintaining network integrity. This minting process helps balance the AVAX burned through transaction fees. Although AVAX is still well below its total supply cap, the token has always been an inflationary asset.
Additionally, Avalanche does not penalise dishonest validators by taking away a portion of their staked tokens (slashing) for negligent or malicious behaviour. Bad actors, however, are disincentivised as they will receive no rewards while wasting the nodes’ computing resources.
Use Cases of the Avalanche Blockchain
Avalanche blockchain offers participants the future with several benefits in ways impossible without a fast, flexible blockchain. Let’s look at some examples of Avalanche’s use cases!

1. Lemonade (Crop Insurance)
Access to insurance can be challenging for many, but Avalanche-powered automation is helping change that. Lemonade utilises oracles to monitor weather conditions and smart contracts to execute payments, enabling small-scale farmers in Kenya to secure crop insurance through an Avalanche-based app. Farmers can register using a smartphone and activate policies for just a few dollars. If adverse weather conditions arise, payouts are automatically distributed to thousands of farmers, providing essential financial protection. This innovation comes at a crucial time, as some insurers are scaling back coverage due to climate change—such as State Farm ceasing home insurance in wildfire-prone California.
2. Deloitte (Disaster Relief)
Deloitte oversees FEMA Public Assistance payments, ensuring state, local, and nonprofit organisations receive funding for disaster relief. The process, historically complex and time-consuming, is streamlined using Avalanche. By integrating Avalanche’s blockchain technology, Deloitte enhances automation, security, and transparency in managing disaster aid applications. As natural disasters increase in frequency due to climate change, Avalanche is proving to be an essential tool for relief efforts.
3. Dreamus (Event Ticketing)
Dreamus, a subsidiary of SK Planet, South Korea’s major entertainment company, has adopted Avalanche for its ticketing app, OK Cashbag. The app serves 21 million users within the country’s $230 million ticketing industry. By leveraging Avalanche, ticketing transactions become more efficient and transparent. The blockchain provides an immutable record, helping verify ticket authenticity, reduce scalping, and prevent fraud in secondary markets.
4. Intain (Structured Finance)
The structured finance market, worth trillions, faces inefficiencies related to transparency and liquidity. Intain aims to address these challenges with IntainMARKETS, a tokenised asset marketplace built on an Avalanche Subnet. This platform helps lenders seeking capital connect with a broader range of issuers, while investors benefit from a streamlined digital marketplace. By utilising Avalanche, all participants gain increased confidence in the integrity and accessibility of financial data.
5. Gunzilla (Gaming)
Avalanche is playing a role in the evolution of gaming with Off the Grid, an upcoming AAA Battle Royale title that integrates Web3 elements. The game, previewed by top streamers, introduces a play-to-own system, allowing players to earn digital assets tied to in-game achievements. By leveraging Avalanche, Gunzilla provides a fast, scalable, and immersive gaming experience, further pushing the boundaries of blockchain-powered gaming.
6. TYB/Shopify (E-commerce & Loyalty Programs)
TYB, a community-driven loyalty platform, is using Avalanche to empower Shopify merchants with Web3 functionality. The platform enables businesses to reward customers for social media engagement, referrals, and product reviews. By integrating Avalanche, TYB allows brands to seamlessly create digital collectibles, assign perks to holders, and distribute them to fans, fostering stronger connections between businesses and their customers.
7. Blockticity (Supply Chain & Certification)
Every year, over $4.5 trillion worth of goods move through the supply chain with fraudulent documentation. Blockticity is leveraging Avalanche to enhance transparency by issuing tamper-proof certifications as NFTs. After a product is tested, a QR code linking to an Avalanche NFT is printed on it. When scanned by vendors or consumers, this NFT confirms the product’s authenticity. Blockticity has already issued certifications for $275 million worth of hemp, cannabis, and related goods and is now expanding to other industries, including sneakers and fresh produce.











